In this document, it mainly introduces the application note of NTP.
Brief Summary
NTP, also named as Network Time Protocol, is used to synchronize PC time. In addition, this protocol can be used to make the PC synchronized with its Server or time source (such as quartz chronometer and GPS), and provide time calibration with high accuracy. (Compared with standard time, the time difference in LAN is less than 1ms, while in WAN, it is about dozens of ms). Finally, it can safeguard malicious protocol attack via encryption. The purpose of NTP is to provide accurate and persistent time in disordered Internet environment.
The premise of providing accurate time is to make sure the time source, that is Universal Time Coordinated(UTC). The NTP can get the time source of UTC from atomic clock, observatory, satellite and Internet. The time will be broadcast according to the level NTP server and all servers will be enrolled into different stratum via the distance to the time source of UTC. The Stratum 1 is located on the top with peripheral UTC access. While for the rest, the stratum of lower will get time from the upper; however, the total of stratum should be controlled within 15. Logically, all these servers are mutually connected with a form of stagged structure and the Stratum-1 serves as the base of the overall system. The host of PC is usually connected to multiple time servers and filters time of different server via statistics to select the optimal path and source for sake of calibrate host time. The NTP will serve as usual even if it is a failure for the host to get connection with certain time server for a long time.
In order to prevent the malicious damage to time server, the Authentication mechanism is deployed in NTP. It will check whether information is actually coming from the claimed server and check the return path of the data to provide protection against interference. The time included in the synchronous message of NTP time is Greenwich mean time (GMT), which starts from 1900.
About API
For detailed API, please refer to QuecPython-ntptime-NTP Time Service
Function realization
For NTP time service, you should get time from NTP server. Therefore, there is a need to connect network beforehand. In this document, we just take the access to network via SIM card as an example.
Step 1
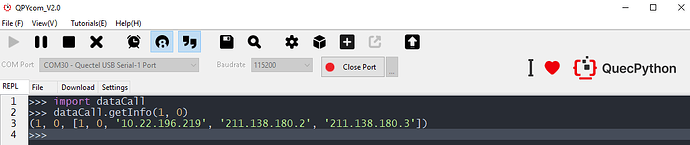
Prepare one usable SIM card, plug in, power on and wait for the automatic dial up. Take EC200U-EU as an example. After automatic dial up, verify whether it is a success via following method:
Figure 1: The verification of data call is a success
Step 2
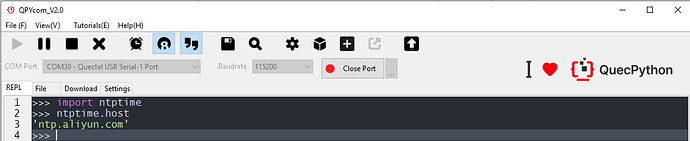
Import ntptime module and return to the current NTP server, which is ntp.aliyun.com by default.
Figure 2: Current NTP Server
Step 3
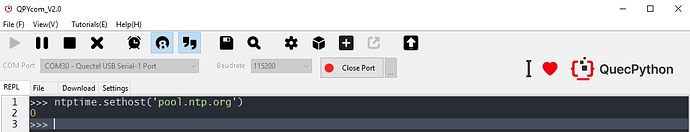
Set NTP server. If it is a success, which will return 0, while it is a failure, which will return -1.
Figure 3: Set NTP Server
Step 4
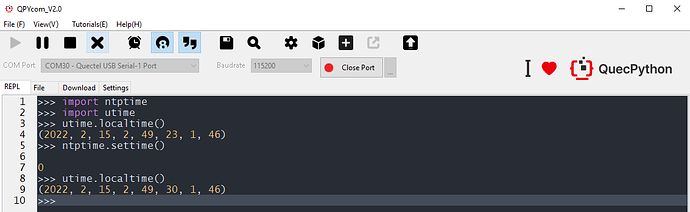
Synchronize NTP time via ntptime.settime. If it is a success, which will return 0, while it is a failure, which will return -1.
As for the time service result, it is available to verify via utime.localtime(). The current time with a tuple- (year, month, mday, hour, minute, second, weekday, yearday) will be returned once execute utime.localtime(). For detailed API, please refer to [https://python.quectel.com/wiki/#/en-us/api/pythonStdlib?id=utime-time-related-functions).
The returned time is UTC via ntptime.settime(), however, the Beijing time is ahead of UTC for 8 eight, therefore, compared with current time, the time goes back 8 hours.
Figure 4: Success in Time Service
Appendix: Term abbreviation
Tablet 1: Term abbreviation
| Term | Description in English |
|---|---|
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| LAN | Local Area Network |
| NTP | Network Time Protocol |
| RTC | Real_Time Clock |
| SIM | Subscriber Identity Module |
| UTC | Coordinated Universal Time |
| WAN | Wide Area Network |