This document is specialized for the conversion between string and Hexadecimal. Please check the details.
Bitwise operation
First of all, we will learn about bitwise operation. The digitals in PC are saved in a format of binary. While the bitwise operation is aimed at binary. In Python, there are bitwise and operators, bitwise or operators, bitwise xor operators, bitwise not operators, left-shift operators, and right-shift operators. For more details, please refer to Bitwise operation.
Bitwise AND operators
Bitwise AND operators &: If both bits in the compared position are 1, the bit in the resulting binary representation is 1 (1 × 1 = 1); otherwise, the result is 0 (1 × 0 = 0 and 0 × 0 = 0). For example:
>>> a= 60
>>> b= 13
>>> a & b
12
Bitwise OR operators
Bitwise OR |: As long as the one of the corresponding two binary is 1, the result will be 1.
>>> a=60
>>> b= 13
>>> a | b
61
Bitwise XOR operators
Bitwise XOR operators ^: The result in each position is 1 if only one of the bits is 1, but will be 0 if both are 0 or both are 1. In this we perform the comparison of two bits, being 1 if the two bits are different, and 0 if they are the same. For example:
>>> a=60
>>> b= 13
>>> a ^ b
49
Bitwise NOT operators ~
Bitwise NOT operators ~: Take the opposite value of every binary data, which means converting 1 to 0 and 0 to 1. it is similar with ~x to -x-1.
>>> a=60
>>> ~a
-61
Left-shift operators <<
Left-shift operators <<: Move all binaries to the left for several bits, which are assigned by the figure on the right, the most significant bit will be discarded and the lowest significant bit will be supplemented by 0.
>>> a=60
>>> a << 2
240
Right-shift operators >>
Right-shift operators >>: Move all binaries to the right for several bits, while the figure on the right assigned the shift bits.
>>> a=60
>>> a >> 2
15
String and HEX
The package of conversion of string and HEX
As for the mutual conversion between string and HEX, we provide one package since there is none in Python.
str_test = 'Quectel build a smarter world'
class String:
def to_hex(a, b=""): # Realizable function: convert to HEX format, it is also available to add the needed separator
Hex = ''.join([hex(ord(c)).replace('0x', b) for c in a])
return Hex,len(a)
def from_hex(a,b=''): # Realizable function: convert to STR. If there exists separator, add parameter conversion.
Str = ''.join([chr(int(c.replace(b, ''), 16)) for c in [a[i:i+2+len(b)] for i in range(0, len(a), 2+len(b))]])
return Str
hex_test = String.to_hex(str_test)
print(type(hex_test[0]))
print(hex_test[1])
print(hex_test)
hex_test = str(hex_test[0])
str_test = String.from_hex(hex_test)
print(str_test)
Application of conversion between string and HEX.
Of course, the converted HEX still can’t receive and analyze via serial interface, therefore, further conversion is needed. Take EC600SCNLB as an example, we will carry out a simple test based on it.
str_test = 'Quectel build a smarter world'
def str_to_hex(s):
list_hex = ' '.join([hex(ord(c)) for c in s]).split()
list = [int(i,16) for i in list_hex]
bytearr = bytearray(list)
return bytearr
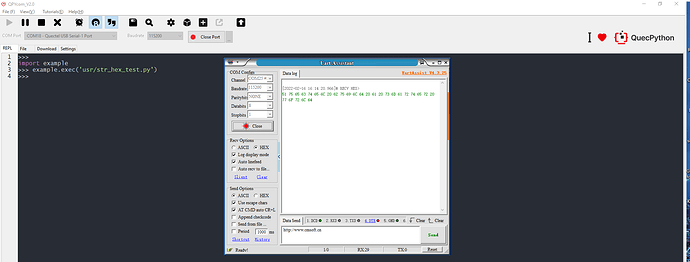
hex_test = str_to_hex(str_test)
1. Compile following codes and name it as str_hex_test.py.
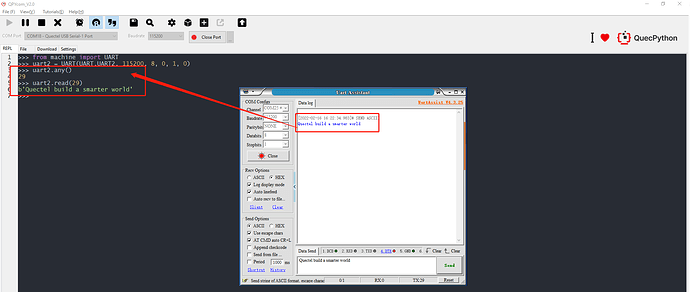
from machine import UART
uart0 = UART(UART.UART2, 115200, 8, 0, 1, 0)
str_test = 'Quectel build a smarter world'
def str_to_hex(s):
list_hex = ' '.join([hex(ord(c)) for c in s]).split()
list = [int(i,16) for i in list_hex]
bytearr = bytearray(list)
return bytearr
hex_test = str_to_hex(str_test)
uart0.write(hex_test)
2. Download above files into the module and run, then enable serial port debugging tool. (Here, it is the UartAssist that is used)
- Run the program and check the result in serial port tool.
Tips:
If received via ASCII, there will be displayed with a form of string.
4. For module serial port reception: Whether the serial port tool sends ASCII or HEX data, it is the bytes data that read by serial port.
Encode and Decode
For encoding and decoding, ASCII, UTF-8 and GBK are widely used, as for python, it is embedded with corresponding package. Hence, you can just take the encode and decode as a reference.
import ubinascii as binascii
import ustruct as struct
def example(express, result=None):
if result == None:
result = eval(express)
print(express, ' ==> ', result)
if __name__ == '__main__':
print('encode and decode:')
print("str to utf-8", end=': ');
example("u'xiaoming'.encode('utf-8')")
print("utf-8 to str", end=': ');
s_utf = b'\xe5\xb0\x8f\xe6\x98\x8e'
example("s_utf.decode('utf-8')")
print("Similarly, there are encode('gbk'),decode('gbk'),encode('gb2312'),decode('gb2312')")
Conversion between binary and ASCII, Package and unzip.
For Conversion between binary and ASCII and ustruct -Package and unzip the original data type, which has been encapsulated on the FW of the module.